
Yajiao Su, Molin Qin, Jinglin Kong, Quanguo Zhai, Daqiang Yuan*, Zhongshan Liu*, and Yu Fang. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2024, 2400433. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202400433.
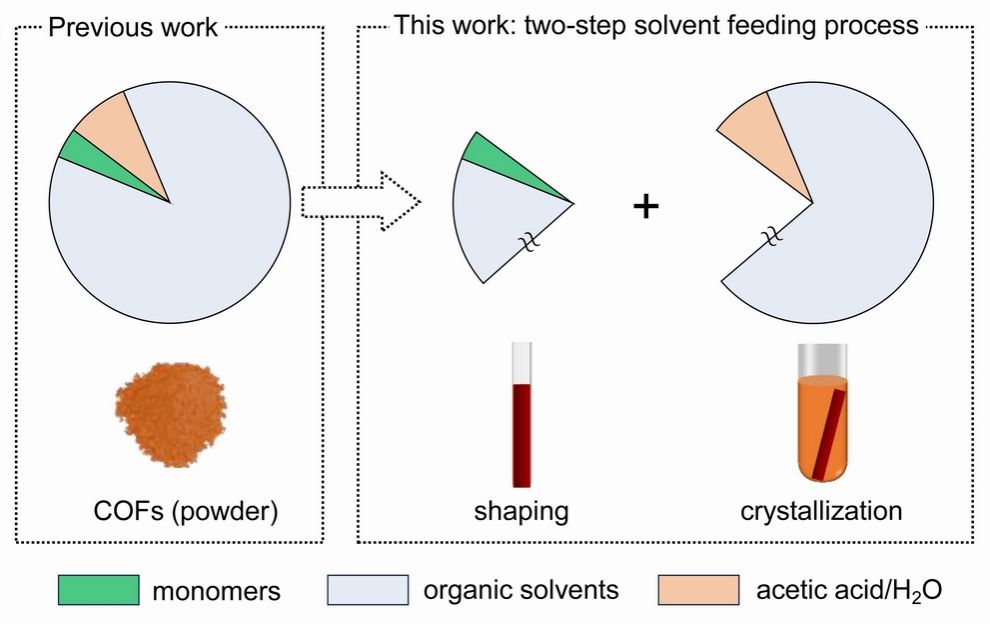
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs), which are ordered porous channels and high surface areas, are ideal gas adsorption and separation materials. Solvothermal synthesis is the predominant method for creating new structured COFs, yet it grapples with challenges in controlling shape and morphology. This issue is attributed to the unregulated solvent-feeding process, which results in rapid polymerization and uncontrolled phase separation.
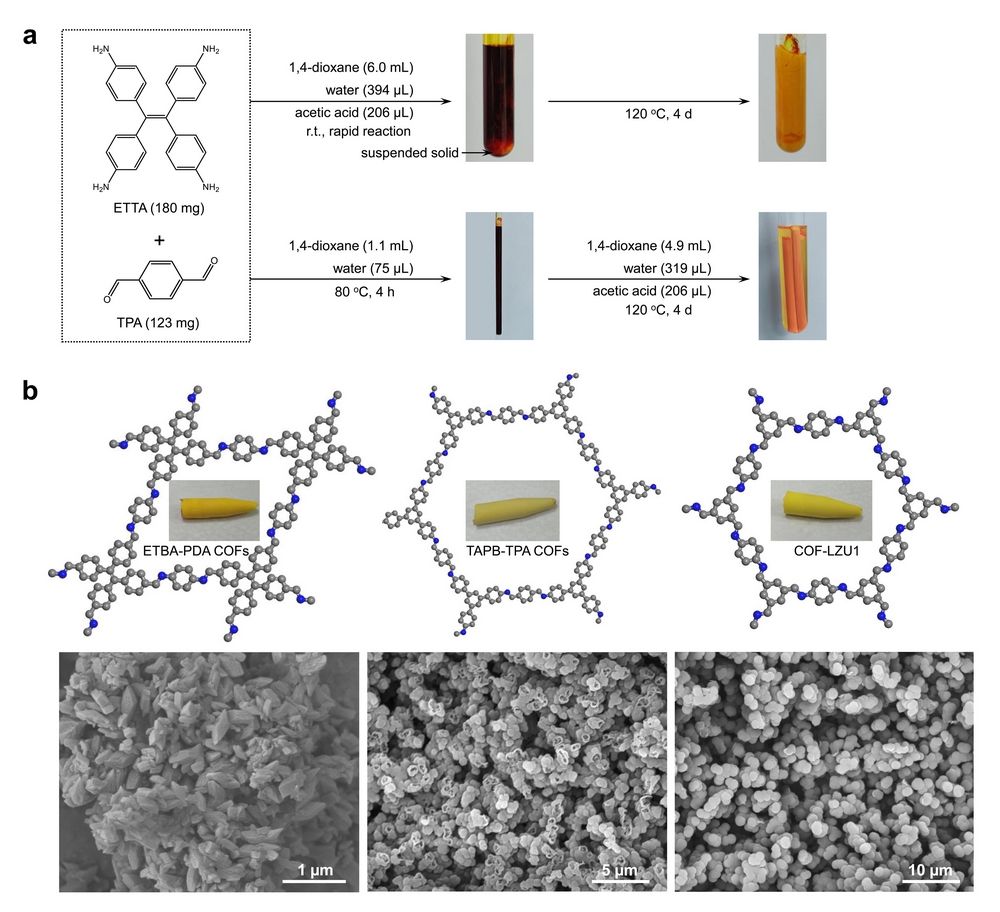
Figure 1. a) One-step (top) and two-step (bottom) solvent feeding processes for solvothermal synthesis of ETTA-TPA COFs; b) The generality of the two-step method
To overcome the abovementioned limitations, we propose a two-step solvent-feeding process to facilitate a solvothermal approach for the synthesis of COF monoliths. we use a small amount of solvent (e.g., 1,4-dioxane) to dissolve monomers (20 wt.%). The polymerization reaction of aldehydes with amines results in amorphous monoliths. The rest of the organic solvents, acetic acid, and water are added for crystallization. By combining this two-step solvent feeding process with the conventional solvothermal method, preparation conditions (e.g., solvent composition, reaction temperature and time) do not need to be re-optimized and four COF monoliths with hierarchical porosity are achieved.
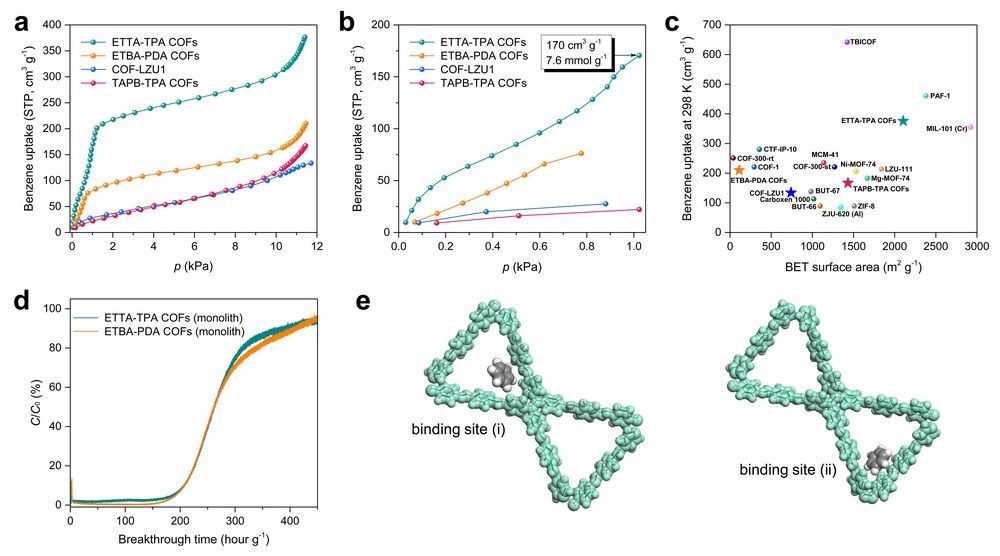
Figure 2. The application of COF monoliths in the adsorption and removal of benzene
Leveraging the hierarchical porosities and conjugated frameworks, we have demonstrated the application of COF monoliths in the adsorption and removal of benzene. The ETTA-TPA COFs monolithic material had a high adsorption capacity of 16.8 mmol g-1 for benzene, and especially the adsorption capacity reached 7.6 mmol g-1 under the low-pressure condition of 1 kPa, which was superior to most of the porous materials in terms of adsorption performance.
In summary, we have successfully demonstrated a two-step solvent-feeding process that enables the solvothermal method for shaping COFs. Our research provides a promising tool for producing COFs with modulated shapes, which is crucial for advancing their practical applications.
First Author: Su Yajiao, master’s candidate, Shaanxi Normal University
Correspondence Authors: Dr. Liu Zhongshan, Shaanxi Normal University, Dr. Yuan Daqiang, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Full Text Link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.202400433