
Jiashuang Yao#, Chun Yang#, Ruijuan Wen, Taihong Liu*, Liping Ding*, Zhen Yao, Yu Fang. ACS Sens. 2024, DOI: 10.1021/acssensors.4c00787
Illicit drugs have seriously endangered public health and social safety because of their wide variety, constant structural renewal, vague legal definitions, and rapid adaptation to legal restrictions. Nowadays, a variety of synthetic cannabinoids and new psychoactive substances (NPSs) have drastically appeared on the global market. The World Drug Report 2023 launched by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime noted NPSs in the global market increased in 2021 after several years of stabilization and a cumulative number of 1184 substances in 2022. Presently, extensive efforts have been made to efficiently detect illicit drugs. These illicit drugs are detected via popular techniques such as high−performance liquid chromatography, gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC−MS), surface−enhanced Raman spectroscopy, fluorescence, and electrochemi−luminescence. However, detection methods for certain aspects of illicit drugs, especially the rapid structural modifications of NPSs, are still scarce. In situ and on−site detection evoked challenges for traditional techniques owing to various drawbacks such as time −consuming, slow response, complicated operations, and bulky and sophisticated equipment. Presumptive tests are critical for prompt qualitative identification of a suspected substance in real−life scenarios, enabling immediate action at the scene. Thus, the first step for the rapid screening of suspected substances in field tests involves the use of drug testing kits or portable devices. Therefore, developing efficient, fast, and on−site analytical strategies for detecting trace illicit drugs is highly desirable.
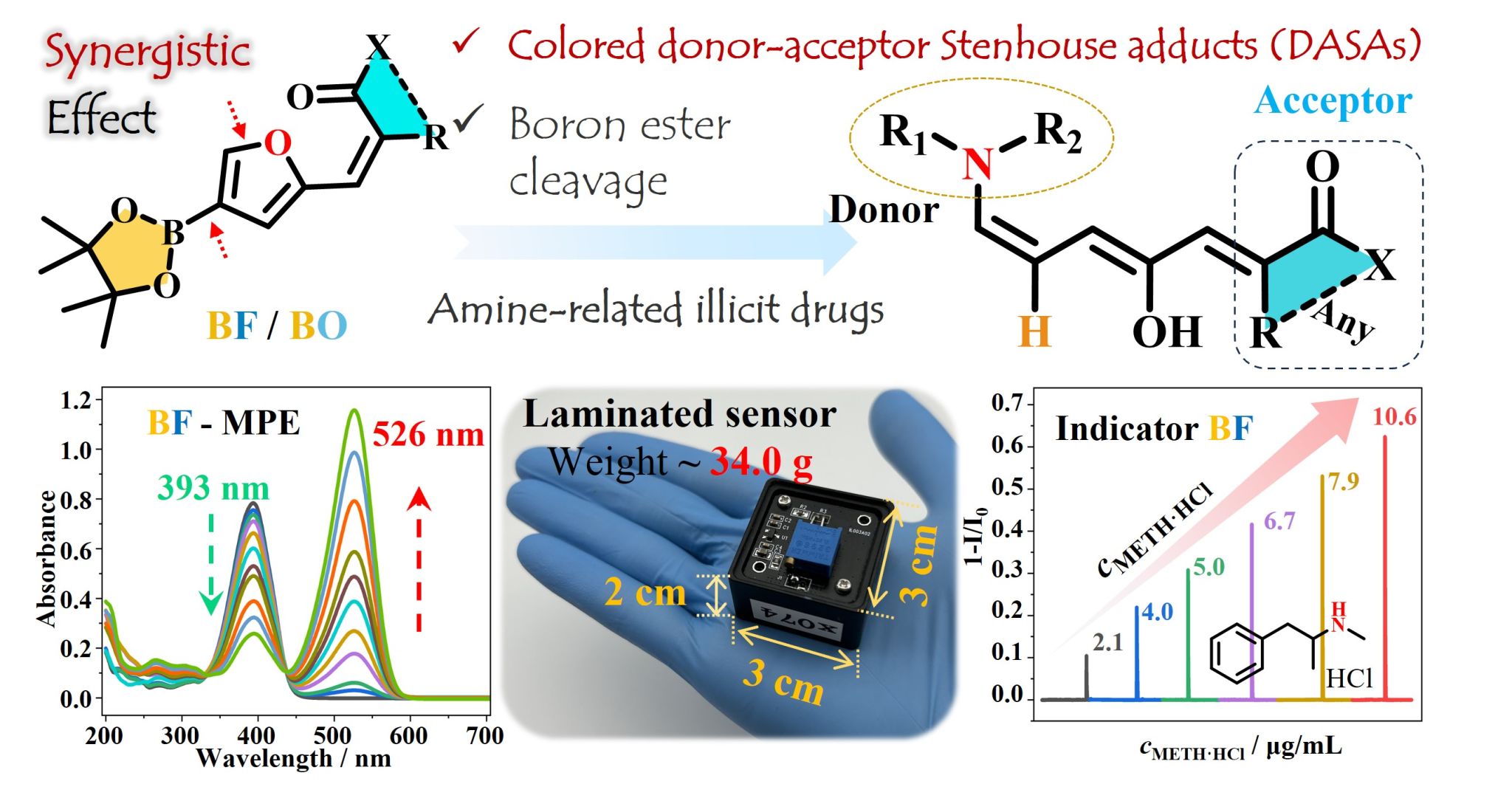
In this study, based on the comprehensive synthetic optimization, two furanic indicators (BF and BO) modified with boron ester groups were synthesized and characterized properly. The indicators with the acceptor units (Meldrum’s acid and CF3-isoxazolone) reacted with the amine-containing illicit drug donors, generating the second- and third-generation DASAs, respectively. Both indicators exhibited distinct color changes from light yellow or colorless to red in the presence of amine-containing illicit drugs, which could be identified with the naked eye. A laminated sensor and prototype sensing platform were successfully realized to detect and screen real illicit drug samples.
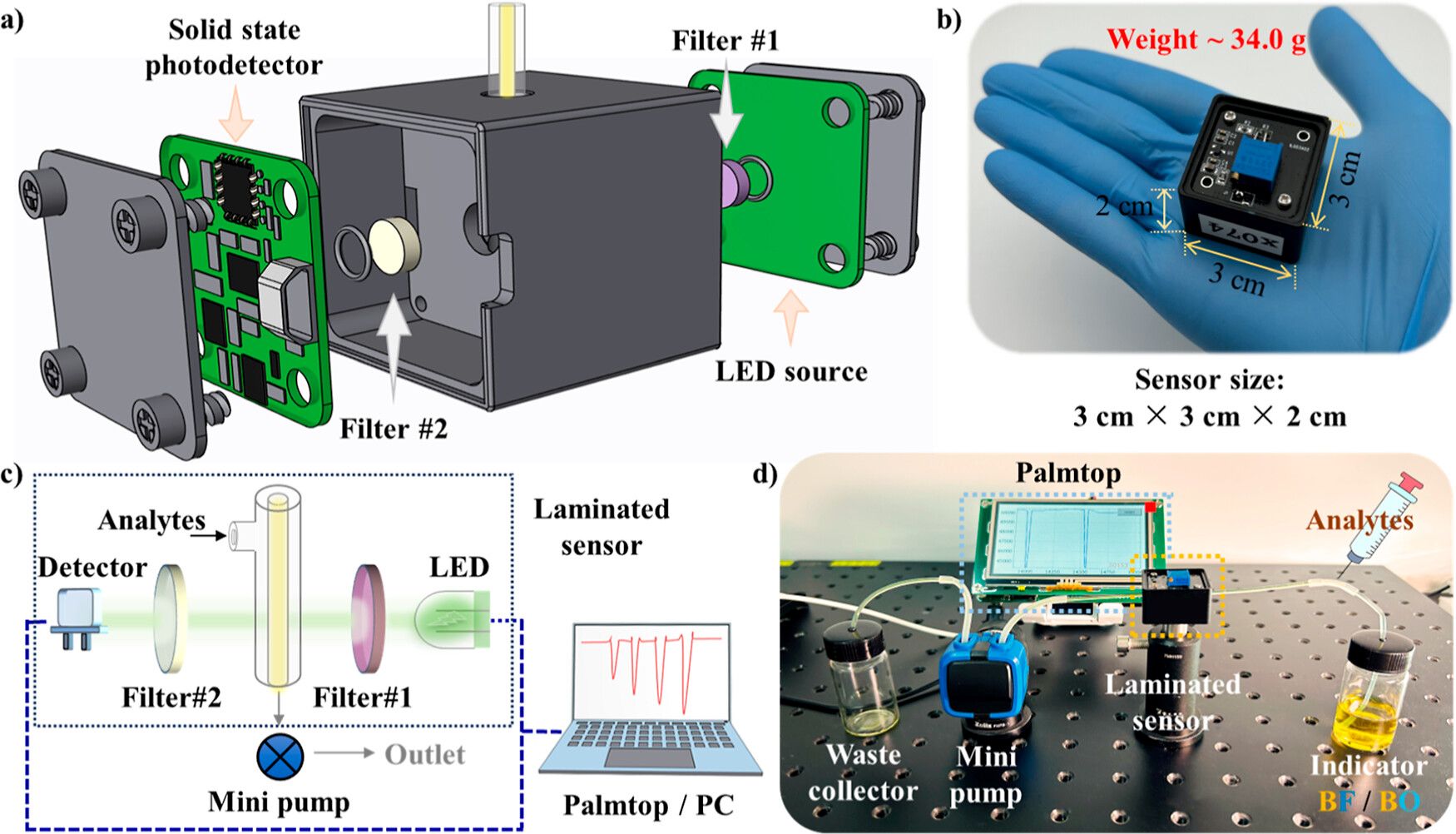
Figure 1. Exploded view of the important apparatus (a), small-size and light-weight (b) of the laminated sensor. Schematic representation (c) and picture (d) of the prototype sensing platform.
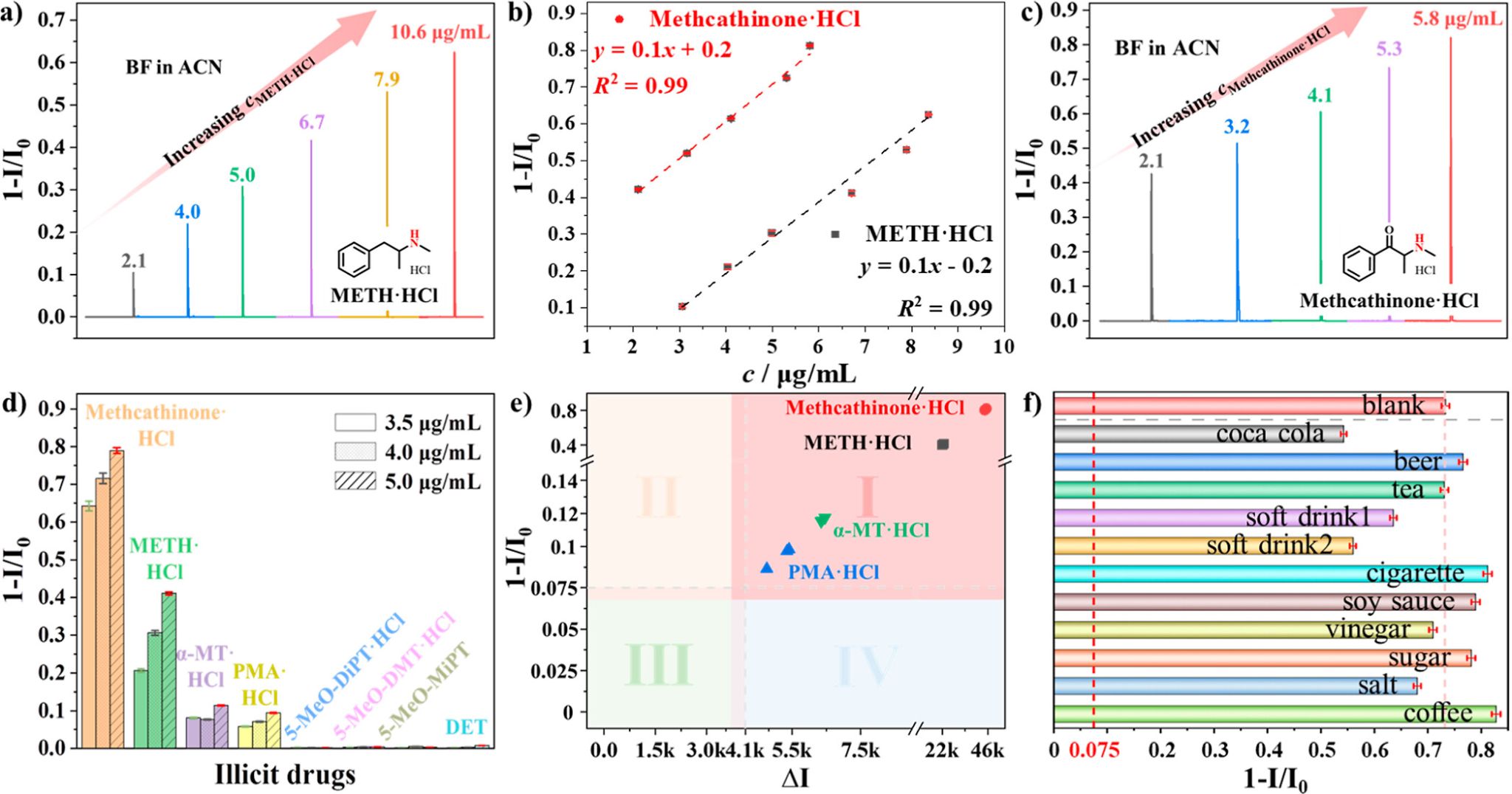
Figure 2. Detection test of the BF-based sensor to the analytes METH·HCl (a) and methcathinone·HCl (c) at different concentrations. (b) Plot of response intensity against the different concentrations of METH·HCl and methcathinone·HCl. (d) Test results of the eight real samples with different concentrations. (e) Efficient screening results based on the integrated sensing platform. (f) Influence of the common interferences to the detection of methcathinone·HCl (4.0 μg·mL-1) using the integrated sensing platform.
This study is to be featured on the cover of the journal ACS Sensors.
First Authors: Yao Jiashuang, master’s candidate, Shaanxi Normal University; Yang Chun, National Anti-Drug Laboratory Shaanxi Regional Center
Correspondence Authors: Assoc. Prof. Liu Taihong, Prof. Ding Liping, Shaanxi Normal University
Full Text Link: https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.4c00787