
Dingfang Hu, Lingya Peng, Wenjun Xu, Shenghui Zhang, Zhongshan Liu, Yu Fang. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8197. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52552-7
Near-infrared transparent films demonstrate important applications in many fields, but how to eliminate light interference from ultraviolet-visible region and how to tackle the trade-off effect between film thickness and transmittance remain as challenges. Herein, we report a near-infrared transparent film that achieves high-efficient combination of thin thickness (16 μm), suitable cut-off wavelength (890 nm), and ideal transmittance (TNIR>90%, TVis<1%). The key component of the film is a complex of a specially designed boron compound containing a perylene monoimide unit (PMI-CBN) with an organic base 1,8-diazabicyclo[5,4,0]undec-7-ene. The complex depicts red-shifted absorption from 709 to 943 nm owing to deprotonation of the N-H group of PMI-CBN.
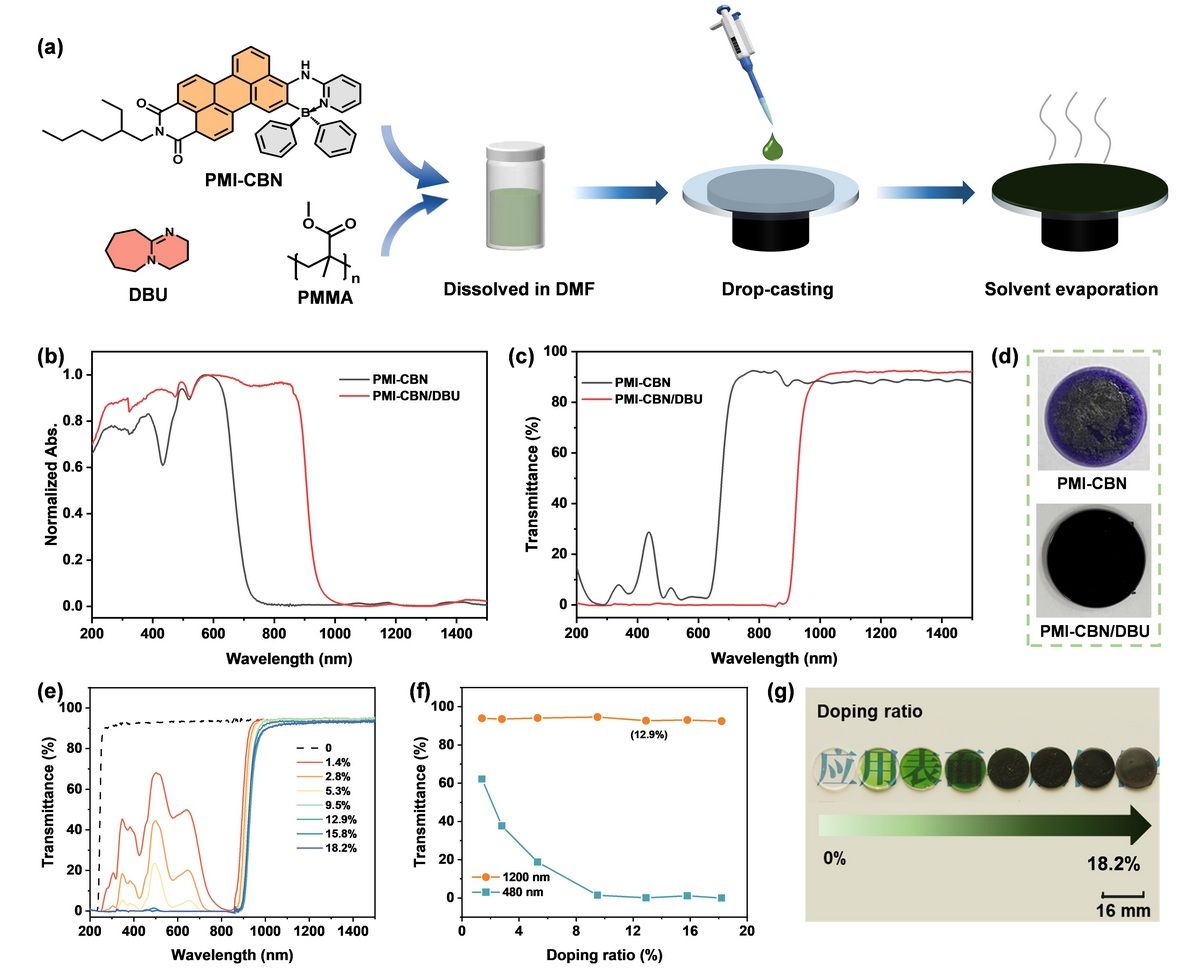
Fig. 1 Preparation and optical properties of NIR transparent film. a Schematic representation of the preparation of the PMMA films of PMI-CBN/DBU. b, c UV-vis-NIR absorption and transmittance spectra of the PMMA films of PMI-CBN and PMI-CBN/DBU. d Photographs of the two films as prepared. e Transmittance spectra of the PMI-CBN/DBU/PMMA films with varying doping ratios of PMI-CBN absorber. f Plots of the transmittances recorded at 480 and 1200 nm versus PMI-CBN absorber doping ratios. g Photographs of the PMI-CBN/DBU/PMMA films with doping contents varied from 0 to 18.2 wt.%.
The obtained PMI-CBN/DBU complex was dispersed in a polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) matrix, forming a flexible, self-standing composite file with adjustable thickness. This film exhibits excellent photochemical stability, heat resistance, and moisture resistance. As an application demonstration, this innovative near-infrared transparent film has been successfully used in night vision imaging and information encryption. We believe that this near-infrared transparent film has broad application prospects in fields such as flexible electronic devices.
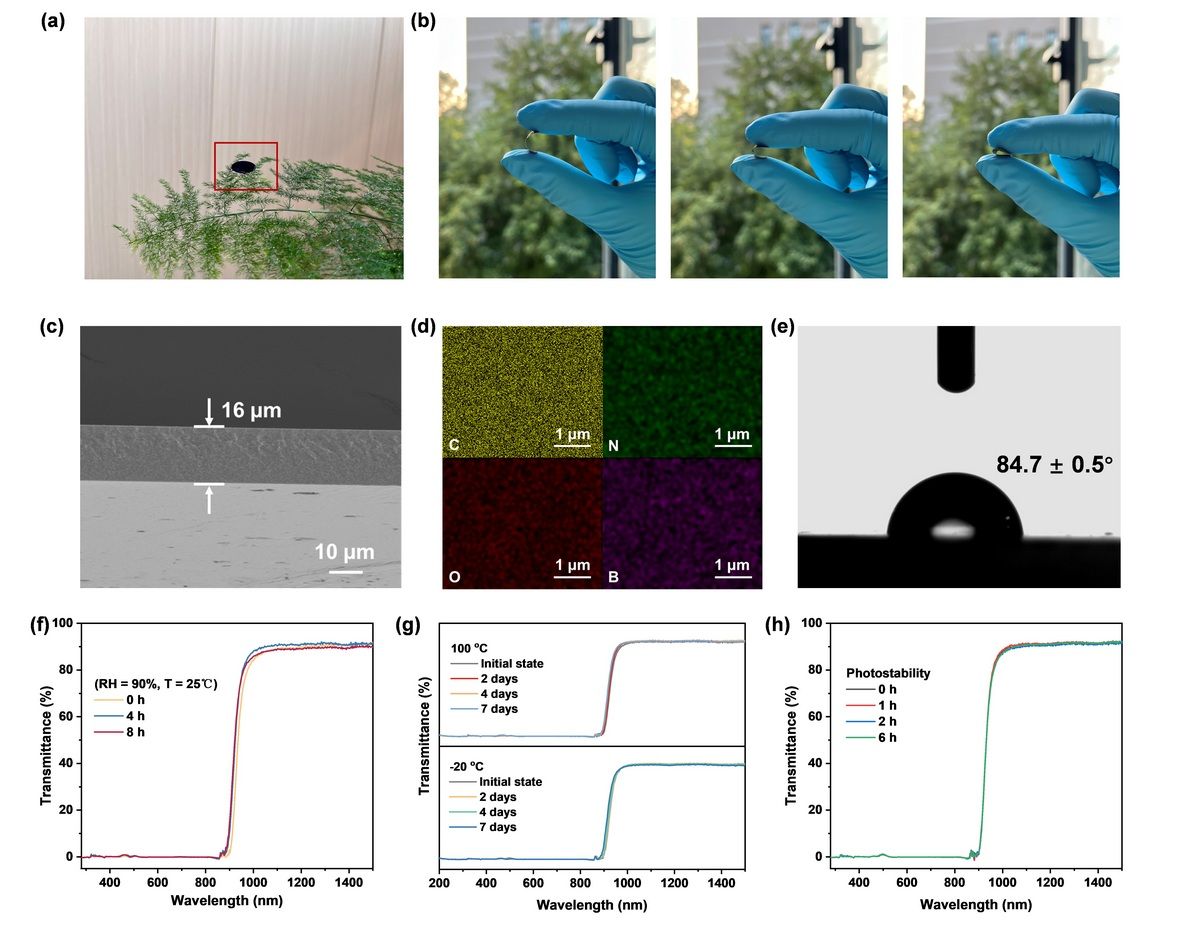
Fig. 2 Flexibility, uniformity and stability tests for NIR transparent film. a Photograph of the self-standing PMI-CBN/DBU/PMMA film. b PMI-CBN/DBU/PMMA film of different bending angles. c Cross-sectional SEM image of the PMI-CBN/DBU/PMMA films. d EDX mapping images of the PMI-CBN/DBU/PMMA films, where the capital letters of C, N, O, and B represent carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and boron elements, respectively. e Water contact angle test for the PMI-CBN/DBU/PMMA film. f and g Humidity and temperature stability of the PMI-CBN/DBU/PMMA film. h Photo-stability of the PMI-CBN/DBU/PMMA film under 1 kW⸳m-2 illumination.
First Author: Hu Dingfang, doctoral candidate, Shaanxi Normal University
Correspondence Authors: Prof. Fang Yu, A/Prof. Liu Zhongshan, Shaanxi Normal University
Full Text Link: https://rdcu.be/dUo8I