
Huizhen Han#, Shiyi Tao#, Yu Sun, Yuxin Luo, Yulian Zhao, Somnath Mukherjee, Yi, Ma*, Xin Bo*, Zenglin Wang*; Adv. Sustainable Syst. 2024, 2400815. DOI:/10.1002/adsu.202400815
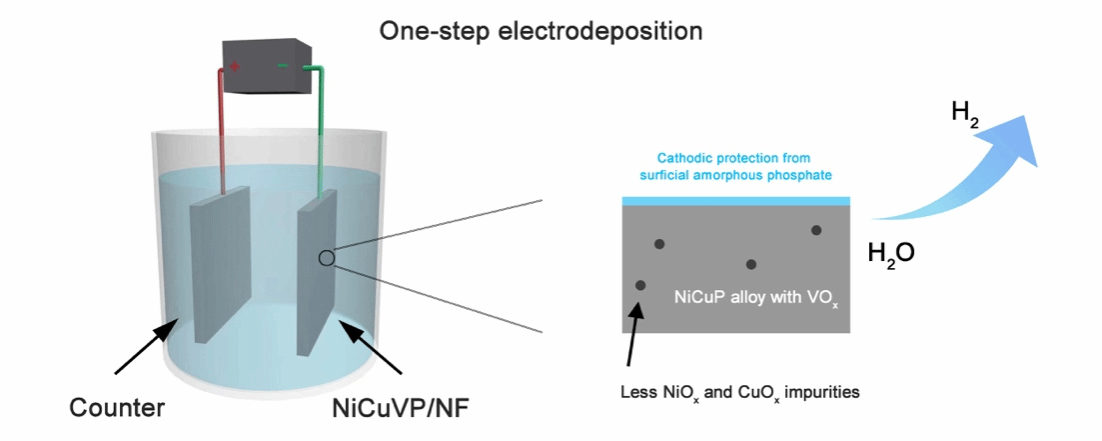
The concentrated alkaline passivates the monolithic electrode for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in the alkaline water electrolysis (AWE) industry. Herein, a surface engineering of cathodic protection via one-step co-electrodeposition of P into NiCuV is presented and the achieved monolithic electrode exhibits an enhanced electrochemical catalytic behavior and constant durability with a feedback potential of -0.75 V versus the reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) under an extremely high current density of 1A cm-2 for more than 270 h in alkaline media. The strategy of cathodic protection optimizes the charge density redistribution by forming a phosphate surface layer. This preserves the particular metal (alloy) phase from oxidation while also modulating the heterarchical porous structure through P incorporation. Furthermore, an anion-exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) with the NiCuVP serving as the HER catalyst and the NiFeCr LDH as the OER catalyst is constructed, which exhibits a current density of 912 mA cm-2 at 2 V at 80 °C with 30 wt.% KOH electrolytes. The resultant factors for activity and durability such as the electrochemical specific area, redox behaviors and surface hydrophilicity are also systematically discussed. This research presents a practical protocol for the anticorrosion and active enhancement of AWE and AEMWE cathodes.
Co-first Authors: Han Huizhen and Tao Shiyi, Master’s candidates, Shaanxi Normal University
Correspondence Authors: A/Prof. Ma Yi, A/Prof. Bo Xin, Prof. Wang Zenglin, Shaanxi Normal University
Full Text Link: https://doi.org/10.1002/adsu.202400815