
Binbin Zhai, Jiaqi Tang, Jianfei Liu, Hongyue Wang, Kaiqiang Liu, Junxia Peng*, Yu Fang*. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2023, 647, 23-31.

Due to its nondestructive, label-free, ultrahigh sensitivity and the vibrational fingerprint-based discriminative capability, surface-enhanced Raman scattering technology has always been a powerful detection method and has been widely used in multiple fields. Although scientists have prepared highly sensitive SERS substrates through various methods, production of uniform and reproducible SERS substrates remains a challenge. Generally, SERS substrates with noble metal nanostructures possess higher sensitivity compared to semiconductors. The top-down methods such as thermal deposition and e-beam evaporation have great advantages in the preparation of uniform and reproducible SERS substrates, but it requires expensive equipment and harsh experimental conditions. The bottom-up wet-chemical methods are relatively simple and cost-effective, but prepared SERS substrates have poor uniformity due to the easy aggregation of metal nanostructures.
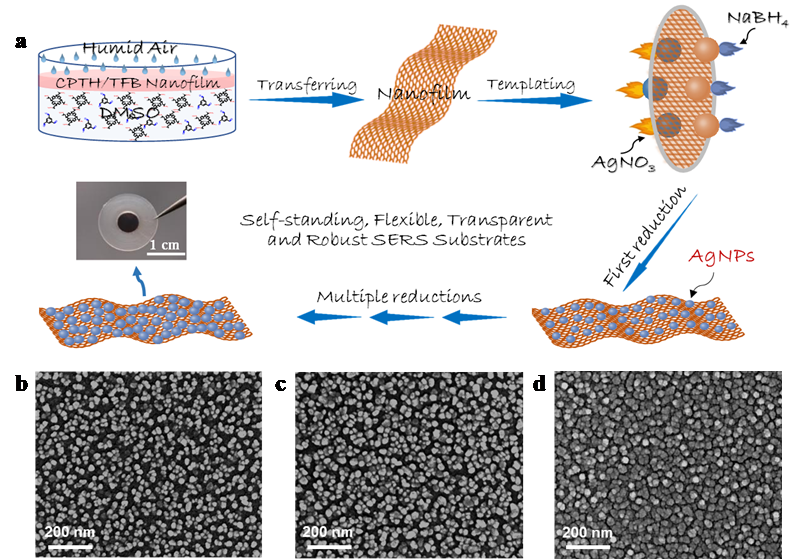
Figure. 1 a) Schematic diagram of the SERS substrates preparation process. b-d) SERS substrates with different the sizes and gaps of prepared AgNPs by refreshing solution times.

Figure. 2 a-c) Self-adhesive, flexible, and scalable preparation of SERS substrate. d-f) The detection ability of SERS substrate for analytes.
Herein, we report a template-based strategy for the strictly controllable and handily scalable preparation of a very uniform SERS substrate, Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs)/nanofilm, where the template used is a flexible, transparent, self-standing, defect-free and robust nanofilm. The nanofilm separates the solution of AgNO3 from that of NaBH4, restricting on film growth of AgNPs. The sizes of AgNPs and the gaps between them can be readily tuned via adjusting the dosages of the reactants and the reaction time. Importantly, the obtained SERS substrates are highly self-adhesive, allowing on-site and in-situ SERS detection of complicated samples. The enhancement factor (EF) of the substrate for rhodamine 6G could reach 5.8×1010 with a detection limitof 1.0×10-15 mol L-1. Moreover, 500 bending tests and one-month storage showed no observable performance degradation, and up to 50.0 cm2 scaled-up preparation depicted negligible effect upon the structure and the sensing performance. The real-life applicability of AgNPs/nanofilm was demonstrated by the sensitive detection of tetramethylthiuram disulfide on cherry tomato and fentanyl in methanol with a routine handheld Raman spectrometer. This work thus provides a reliable strategy for large area wet-chemical preparation of high-quality SERS substrates.
First Author: Zhai Binbin, doctoral candidate, Shaanxi Normal University
Correspondence Authors: Prof. Fang Yu, Assoc. Prof. Peng Junxia, Shaanxi Normal University
Full Text Link: www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021979723009335?via%3Dihub